This is a longer post than my usual one’s. I wrote this piece when I was accountable for SEO for one of the eCommerce retailers in the area. Most of it is still relevant today for someone who wants to understand the basics of SEO.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the science of enabling the discovery of web pages by the search engines and to make them rank higher for keywords of interest in the natural search results.
Wikipedia defines science as “Science (from the Latin scientia, meaning “knowledge”) refers to any systematic knowledge-base or prescriptive practice that is capable of resulting in a prediction or predictable type of outcome”. Even though we have defined SEO as a science, when it comes to achieving higher ranking for your web pages, the outcomes are not predictable since the search engines hold their ranking algorithms secret and the website owners have to typically try and unlock some elements of it through continuous experimentation and measurement.
SEO targets the natural search results and unlike sponsored links, the traffic from natural search results is free. Search engines display the list of websites that their algorithm determines as the most relevant for the keyword and are typically displayed in the order of relevance to the keyword. There is an element of trust that the users have developed (though debatable) over the last decade on the quality of the natural search results and traffic from natural search results tend to generate more downstream clicks than from sponsored links.
In order to understand how to go about optimizing one’s website for search engines, it is important to understand how search engines work, their limitations and the factors that can enable your website to rank higher than your competitor’s website. The following sections provide you with the information required to get a good understand of those concepts.
How do Search Engines work?
There are 3 steps that need to happen before your website can receive any traffic from search engines. The steps are depicted pictorially below and the description of each of the steps follows the picture.
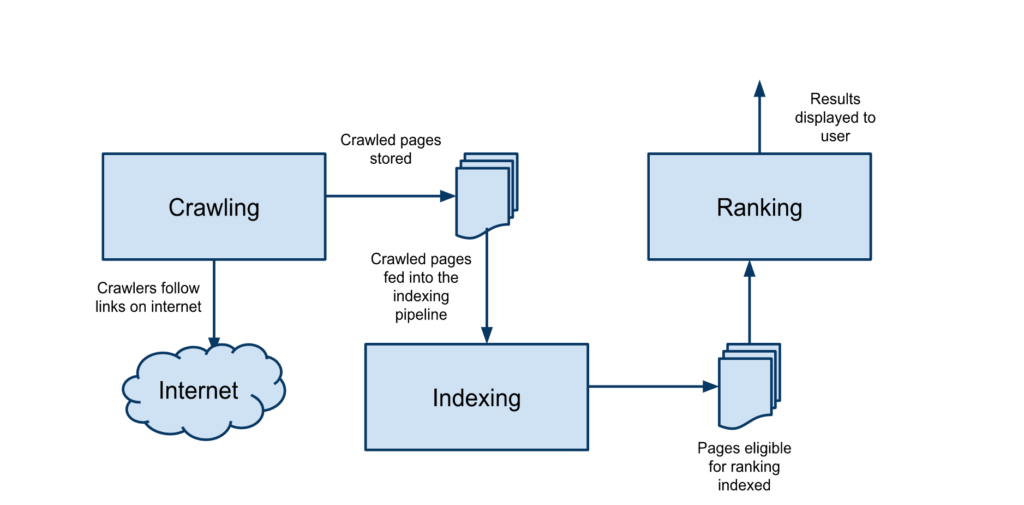
Crawling is the first step in driving traffic from Search Engines. Crawling generically refers to the process of discovery of pages on a website by the Search Engines. Before a Search Engine can rank a web page they need to discover and retrieve the content of the web page and store it in their data store. They have automated agents or crawlers commonly known as Robots that are continuously discovering new pages on the Internet and updating the known pages in their data store with the updated content.
Indexing
Indexing is the process of ingesting the content retrieved by the crawlers into the Search Engine’s index. Indexing is the process of collecting, parsing and storing data to facilitate fast and accurate retrieval of content. Once a web page is in the index, the page is eligible to be ranked for a user entered keyword.
Ranking for a Keyword
Once a web page is in a Search Engine’s index, it is eligible to be ranked for a keyword. When a user enters a keyword on the Search Engines, the ranking algorithms sort through the million of pages in their index and return the most relevant web pages for the keyword.
Common SEO Jargon
Page Title: Page Title is what appears in the blue bar at the top of the browse window. Page title is in the <title> tag in the <HEAD> block of the HTML. Page Title is also used as the link text in the Search Engine Search Results (SERP).
Canonical URL: Canonical URL is the normalized URL for a webpage. URL is used as the key for a webpage by the search engines and variations of all URL’s with any parameters in the URL that do not change the behavior or content on the page should be normalized to a single URL. For example, if a webpage http://www.example.com/electronics and http://www.example.com/electronics?fromPage=home display the same content with the parameter “fromPage” used a mechanism to understand the source page the user clicked on then the second parameter is a non essential parameter for search engines. The canonical URL in the above example should be http://www.example.com/electronics and that should be the URL exposed to the search engines and indexed.
Backlink: Links pointing to a page. A Webpages is discoverable due to other pages linking to it, the link to a page from another page is a backlink to the webpage.
Link Equity / Linkjuice: All the backlinks to a webpage.
PageRank: PageRank is a link analysis algorithm that assigns a weight to every webpage on the internet with the purpose of measuring it’s relative importance. Google describes it as “PageRank relies on the uniquely democratic nature of the web by using its vast link structure as an indicator of an individual page’s value. In essence, Google interprets a link from page A to page B as a vote, by page A, for page B. But, Google looks at more than the sheer volume of votes, or links a page receives; it also analyzes the page that casts the vote. Votes cast by pages that are themselves “important” weigh more heavily and help to make other pages “important”.
Domain Authority: Trust and credibility of the domain (i.e is it a well known brand name a link from Amazon.com is likely to weigh a lot more than a link from your own personal blog).
Blackhat SEO: SEO techniques that violate the quality guidelines outlined by the major search engines. An example of a black hat technique is redirecting Robots to a different version of the page.
Cloaking: Cloaking is a specific type of black hat technique that entails showing different content to Robots and Users.
Crawler: Crawler is an automated program used by search engines to discover pages and gather content from those pages on the internet. Also known as Robots
Keyword Spamming: Including keywords either hidden or visible to the customers that are not relevant to the content on the page with the purpose of misleading search engines.
Link Farm: Link Farming is the practice of setting up multiple sites with the sole intention of increasing links to one’s websites.
Link Text: The text that appears in a link on a webpage.
No Follow: The No Follow directive instructs search engines that the authority/trust of the link is not vouched for by the source page. The No Index directive can be set at an individual link level or for the entire page.
No Index: The No Index directive instructs the search engines to not include the current page in their index.
SERP: Search Engine Result Pages is the results page displayed by the search engines for a specific query.
White Hat SEO: SEO techniques that are in compliance with guidelines published by the search engines.

Good overview